INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence term was coined by
John McCarthy in 1956. He defined it as “the science
and engineering of making intelligent machines.” AI is
the branch of computer science which deals with the
study and design of intelligent agents that perceives its
environment and takes actions which maximize its
chances of success. AI may be defined as: “The ability
to hold two different ideas in mind at the same time
and still remain the ability to function”. But AI must
include the learning from past experience, reasoning
for the decision making, inference power and quick
response. Also it must be able to take decisions on the
basis of priorities and tackle complexity and ambiguity.
Machines programmed to carry out tasks, when carried
out by humans would require intelligence, are said to
possess artificial intelligence. AI’s scientific goal is to
understand intelligence by building computer programs
that exhibit intelligent behavior by using symbolic
inference, or reasoning inside the machine. AI definition
is not time-independent. It gives the judgment of any
system by keeping time in mind

Artificial intelligence can be viewed from a variety of perspectives.
From the perspective of intelligence
artificial intelligence is making machines “intelligent” — acting as we would
expect people to act.
The inability to distinguish computer responses from human responses
is called the Turing test.
Intelligence requires knowledge
Expert problem solving – restricting domain to allow including
significant relevant knowledge
From a business perspective AI is a set of very powerful tools, and
methodologies for using those tools to solve business problems.
From a programming perspective, AI includes the study of symbolic
programming, problem solving, and search.
Traits of an AI
Capable of predicting and adapting, AI uses algorithms that discover patterns from huge amounts of information.
Makes decisions on its own, AI is capable to augment human intelligence, deliver insights and improve productivity.
Continuous learning, AI uses algorithms to construct analytical models. From those algorithms, AI technology will find out how to perform tasks through innumerable rounds of trial and error.
AI is forward-looking, AI is a tool that allows people to reconsider how we analyze data and integrate information, and then use these insights to make better decisions.
AI is capable of motion and perception.

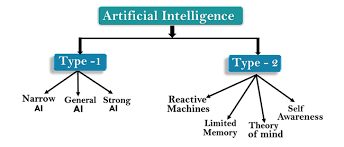
Types of AI
Type 1
Artificial intelligence today is accurately known as narrow AI (or weak AI), it is non-sentient machine intelligence, typically designed to perform a narrow task (e.g. only facial recognition or only internet searches or only driving a car).
However, the long-term goal of many researchers is to create an artificial general intelligence (AGI or strong AI) which is a machine with the ability to apply intelligence to any problem, rather than just one specific problem, typically meaning “at least as smart as a typical human”.
While narrow AI may outperform humans at whatever its specific task is, like playing chess or solving equations, AGI would outperform humans at nearly every cognitive task.
The ultimate hypothetical goal is achieving superintelligence (ASI) which is far surpassing that of the brightest and most gifted human minds. Due to recursive self-improvement, superintelligence is expected to be a rapid outcome of creating artificial general intelligence.
Type 2 (based on functionalities)
Purely Reactive
Reactive machines are basic in that they do not store ‘memories’ or use past experiences to determine future actions. They simply perceive the world and react to it. IBM’s Deep Blue, which defeated chess grandmaster Kasporov, is a reactive machine that sees the pieces on a chess board and reacts to them. It cannot refer to any of its prior experiences, and cannot improve with practice.
Limited Memory
Limited Memory machines can retain data for a short period of time. While they can use this data for a specific period of time, they cannot add it to a library of their experiences. Many self-driving cars use Limited Memory technology: they store data such as the recent speed of nearby cars, the distance of such cars, the speed limit, and other information that can help them navigate roads.
Theory of Mind
Psychology tells us that people have thoughts, emotions, memories, and mental models that drive their behaviour. Theory of Mind researchers hope to build computers that imitate our mental models, by forming representations about the world, and about other agents and entities in it. One goal of these researchers is to build computers that relate to humans and perceive human intelligence and how people’s emotions are impacted by events and the environment. While plenty of computers use models, a computer with a ‘mind’ does not yet exist. Examples like C-3PO R2-D2 from Star Wars Universe and Sonny in the 2004 film I, Robot
Self-Awareness
Self-aware machines are the stuff of science fiction, though many AI enthusiasts believe them to be the ultimate goal of AI development. Even if a machine can operate as a person does, for example by preserving itself, predicting its own needs and demands, and relating to others as an equal, the question of whether a machine can become truly self-aware, or ‘conscious’, is best left for philosophers. Examples like Eva in the 2015 movie Ex Machina and Synths in the 2015 TV series Humans.
USES OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN EDUCATION
Simplifying administrative tasks
AI can be utilized to streamline many administrative tasks and duties that are currently handled by teachers, such as preparing plans, examination grading, checking homework, etc. Automating these processes can ease the pressure on the teachers, provide them with a birds-eye view over each student’s progress, and let them focus on improving their educational techniques.
Smart content
Smart content is an integral part of the digitized curriculum. Though still in its nascent stage, many schools are striving to make the online curriculum available through different digital platforms to make it more interactive. With AI-based tools, learning materials such as eBooks, audio, and video can be easily categorized and grouped according to the educational plans and even student preferences. This way the learning process and the curriculum are made more student-centric.
Personalized learning
Unlike the traditional education system that usually targets the middle 80% of students and leaves the upper and lower 10% pupils, AI-based systems promise to serve students of all capabilities and discover their full potential. Schools and universities are now utilizing AI in the classroom for personalized recommendations on the sessions, their performance, daily assignments, and even in examinations. Also, students now have access to AI-powered smart tutoring systems where they have the advantage of personalized study plans, accessible from any user device or location.
Voice assistants
Who would have thought that voice assistants like Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Home can change the teaching equations? These interactive voice assistants can assist with different learning material even in the absence of a teacher, and have made learning possible anywhere and anytime. Apart from supporting learning, integration of such voice assistant technology within the school campus system can make following schedules a fun and engaging experience for the students.
Global learning
Technology is bridging and connecting people of different geographical locations. This has turned out to be a boon for the students as they can now easily communicate and share ideas with their peers from around the world. With the help of state-of-the-art AI solutions, several colleges and universities are creating learning platforms for students from different parts of the globe to study together.
AI-based tools are helping them organize classes based on curriculum and customize the experience to match the student’s ethnicity, providing access to education materials within their cultural background. Language translations and automated subtitle creation enable teachers and students to communicate online without any boundaries. The future of global education looks bright as these AI tools get further fine-tuned to support more languages and dialects.
Efficient school management
Besides curriculum and teaching methods, AI technologies can optimize and streamline management processes for educational institutions. For instance, AI-based tools can help in the proper designing and planning of classrooms according to the number of students. With data-driven insights, school management can timely distribute resources to areas of higher demand and cut down on unnecessary expenses.
EXPECTED SPAN OF AI OVER THE NEXT 10 YEARS
In 20 years, AI will automate most of the workforce. As AI learns, it will be able to offer the same value as humans, and it will be able to provide that value instantly and for 100x cheaper.”

CONCLUSION
Not so far in the future, we can expect Artificial Intelligence and machine learning to occupy an integral place in all educational experiences. AI has started to prove its advantages and power in a wide range of educational areas, and it remains to be seen how the technology will empower and enhance overall learning outcomes for all.
REFERENCES
Holmes, W., Bialik, M., & Fadel, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence in education. Boston: Center for Curriculum Redesign.
Roll, I., & Wylie, R. (2016). Evolution and revolution in artificial intelligence in education. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 26(2), 582-599.
Baker, M. J. (2000). The roles of models in Artificial Intelligence and Education research: a prospective view. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Education, 11, 122-143.

Very helpful
LikeLiked by 1 person
Good work done bro
LikeLiked by 1 person
Nice one there!!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Great
LikeLiked by 1 person
Nice work 👌
LikeLiked by 1 person
Awesome 👍
Keep it up
LikeLiked by 1 person
Very educative
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks
LikeLike
Well done. Nice presentation and deta
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks very much
LikeLike
Thanks bro. We are most grateful
LikeLike
Good
LikeLike
Thanks very much
LikeLike
Good job! Keep posting.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks very much for the compliment madam🙏
LikeLike